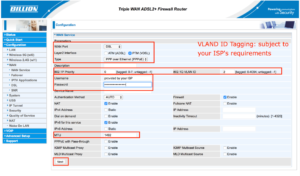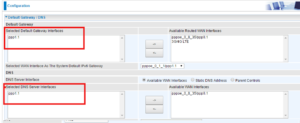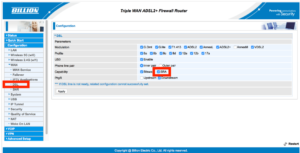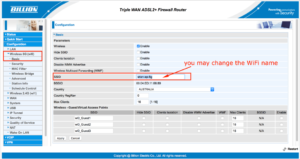
How to connect FTTN and FTTB NBN service
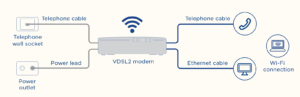
Fiber to the Node (FTTN) and Fiber to the Basement (FTTB). Uses a mix of fiber-optic and existing copper wiring to connect you to the Internet. VDSL or VDSL2 technology is typically used to connect you to the Internet from the fiber connection in the neighborhood or /basement.
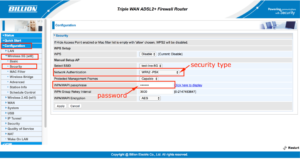
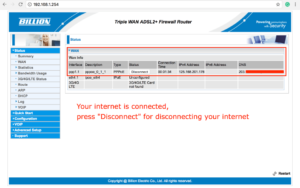
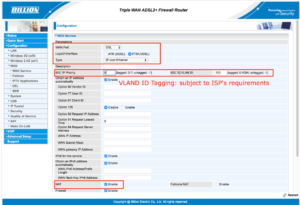
You can use a Billion DSL modem router, such as the Billion 8700 series, 8900 series and 9820NZ.
nbn™ FTTB made easy
All types of nbn™ broadband access network connections that utilise a physical line running to the premises are considered Fixed Line connections. An nbn™ Fibre to the Building (FTTB) connection is generally used when we are connecting an apartment block or similar types of buildings to the nbn™ access network. In this scenario we run a fibre optic line to the fibre node in the building’s communications room, and then we use the existing technology in the building to connect to each apartment.
The fibre node is likely to take the form of a secure cabinet in your building’s communications room. Each cabinet will allow the nbn™ access network signal to travel over a fibre optic line, to the existing network technology present in the building.
nbn™ FTTN made easy
All types of nbn™ broadband access network connections that utilise a physical line running to the premises are considered Fixed Line connections. An nbn™ Fibre to the Node (FTTN) connection is utilised in circumstances where the existing copper phone and internet network from a nearby fibre node is used to make the final part of the connection to the nbn™ access network.
The fibre node is likely to take the form of a street cabinet. Each street cabinet will allow the nbn™ access network signal to travel over a fibre optic line from the exchange, to the cabinet, and connect with the existing copper network to reach your premises.